 |
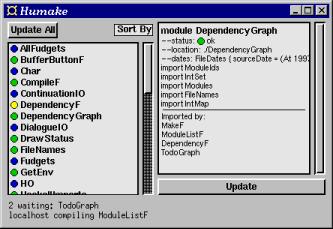
Figure 92. The user interface of Humake.
Figure 92. The user interface of Humake.
In the current version, the user interface shows
dependencyF. It traverses the modules to extract the
module-dependency graph and builds a representation of it. It
also maintains a data structure representing the status of the
compilation process. This structure is chosen so that when a
compilation completes, or a module is updated, a new compilation
can be started as quickly as possible.
The source is about 1200 lines long.
main = fudlogue $ shellF "Humake" humakeF humakeF = loopLeftF ((moduleInfoF>+<parallelCompileF) >==< dependencyF) >==< editorInterfaceF --- GUI fudgets: statusDisplayF = ... --the bottom part of the window moduleInfoF = ... -- the module list, module info and the update buttons --- Non-GUI fudgets: parallelCompileF = filterRightSP >^^=< (statusDisplayF>+<idF) >==< loopThroughRightF (absF ctrlSP) (parServerF hosts compileF) where ctrlSP = ... parServerF :: [id] -> (id->F req resp) -> F req resp parServerF ids serverF = ... -- essentially as in Figure 88 compileF :: String -> F CompilerReq CompilerResp compileF host = ... -- a compilation server editorInterfaceF :: F a String editorInterfaceF = ... -- outputs the name of a file when it is savedFigure 93. Implementation of Humake.